SURVEYS AND GRAPHIC RESTITUTION
supervised and coordinated by:
Eng. Fulvio Fucci
Remote Pilot A1/A2/A3 (*)
Geom. Manuel Pelliccia
(*) REGISTRATION NUMBER: ITA-RP-020655AAA
Laser Scanner
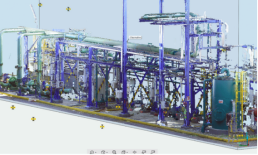
Laser scanner surveying is a well-established three-dimensional digital surveying methodology for surveying the state of civil works, industrial facilities, infrastructure and territory.
Laser scanners are instruments capable of measuring at very high speed the position of hundreds of thousands of points, which define the surface of surrounding objects. What is obtained from this survey is a very dense set of points that is called a point cloud.
Each point contains information describing its position in space (X, Y and Z coordinates) and color (RGB components).
Thus, the Laser Scanner is a direct measurement system because it enables measurements correlated with an instrumental accuracy evidenced by a calibration certificate, which officially documents the results of the measurement.
The laser scanner survey enables the measurement and recording in three-dimensional digital form of the state of affairs of a work of any complexity and size in a way:
- Geometrically and dimensionally complete
- Fast, as the laser scanner can measure up to 1 million points per second
- Precise, as the three-dimensional point cloud reproduces the current state of the work with pinpoint accuracy.
Laser scanner surveying makes it possible to obtain a completeness of information that is impossible to obtain with other instrumentation
In the case of civil works and industrial plants of considerable extent, articulated geometries or development on several levels, laser scanner survey provides a complete and reliable basis for the design and construction of the works.
The point cloud produced by a laser scanner survey is imported into traditional CAD and Building Information Modelling (BIM) software to perform all kinds of visualization, measurement, modeling and design.
What is used for
- Obtain massive surveys without the need for subsequent on-site verification compared with traditional direct surveys.
- More information in the survey.
- Greater speed in acquisition and restitution.
- Possibility of obtaining straightened photo-plans.
- Ability to model surveyed objects in BIM.
Fields of Application
- TOPOGRAPHY: Survey of land, architectural and civil structures.
- ARCHITECTURE: Survey of objects of archaeological and architectural interest.
- BIM: Surveying aimed at 3D reproduction of geometries and properties of surveyed elements.
- MORPHOLOGY: Survey of geomorphological features of the territory and quantification of changes over time.
- VALORIZATION: Surveys aimed at the enhancement and tourist promotion of assets with historical and architectural value.
- PREVENTION: Preventive surveys with legal validity of housing structures and in-progress monitoring.
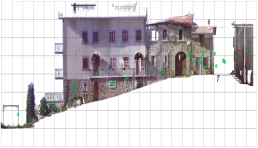
Photogrammetry
It is Based On
- Use of 2D aerial or terrestrial, traditional or digital photographic images taken with a simple camera.
- Identification of metric data in terms of shape, size and position in space of the photographed object or space
- Structure from Motion (SfM): a technique based on "Computer Vision" algorithms extracts notable points from individual photos, inferring photographic parameters and cross-referencing recognizable points on multiple photos, detecting the coordinates in space of those points.
Fields of Application
- Cartography
- Topography
- Architecture
- Archaeology
- Geology
Examples of Photogrammetry
Drone Survey
The use of drones in roof and roofing survey and inspection operations are numerous:
- economic savings
- rapid intervention
- reduction of risks to workers' health and safety
It is no longer necessary to install scaffolding, guardrails, or rent lifting platforms. There are no workers at height and consequently no risk of personnel falling from height or risk of collapse.
L’utilizzo del drone riduce il rischio alla fonte e permette un’idonea progettazione in sicurezza.
Object
- Inspect industrial and civil roofs and coverings that are difficult to access or impractical because they consist of non-bearing slabs
- perform a non-invasive survey without danger of collapse or damage to the roof covering
- view and document the condition of a property in order to assess and schedule maintenance work
- accurately measure and quantify damage